
Symptoms of Atrial Septal Defect
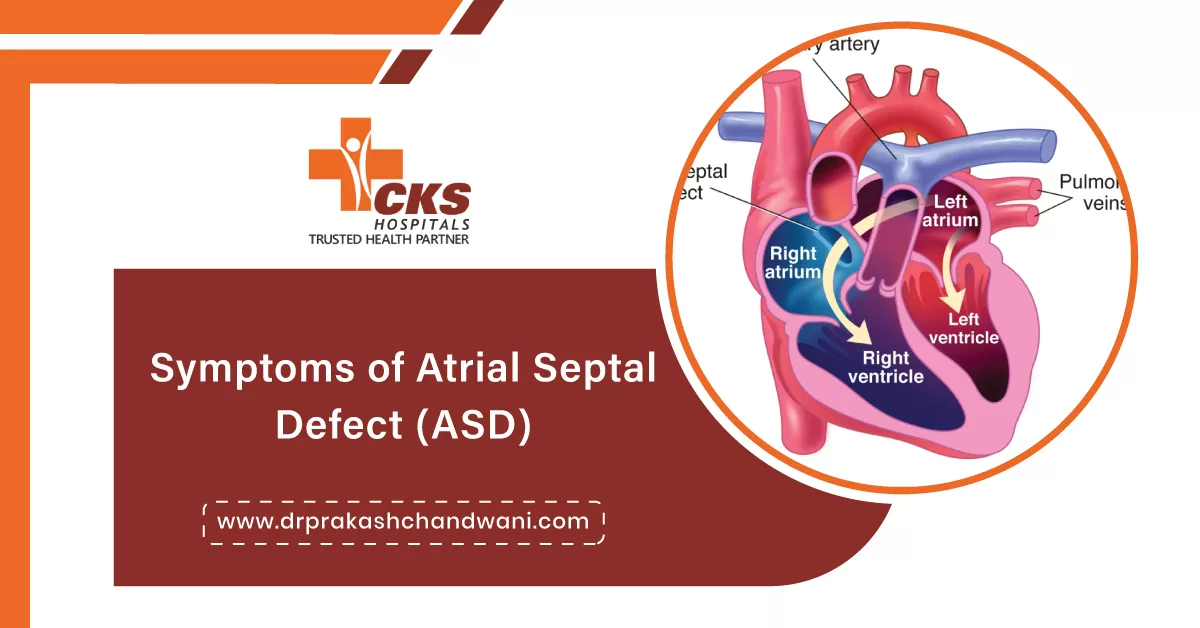
Symptoms of Atrial Septal Defect: Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect characterized by an abnormal opening in the atrial septum, the wall that separates the heart’s two upper chambers (atria). This condition allows oxygen-rich blood from the left atrium to mix with oxygen-poor blood in the right atrium, leading to various physiological complications. While some individuals with small defects may remain asymptomatic, larger defects often result in noticeable symptoms that can affect both children and adults.
The manifestations of ASD can range from mild to severe, depending on the size of the defect and the individual’s overall health. Whenever there is a symptom noticed it is necessary to reach the Cardiologist in Jaipur for treatment. In this article we will help you to know about the symptoms in detail!
10 Symptoms of Atrial Septal Defect:
1. Shortness of Breath:
Individuals with ASD often experience difficulty breathing, especially during exertion. This symptom occurs because the defect allows oxygen-rich blood to flow back into the lungs instead of out to the body, increasing the workload on the heart and lungs. Over time, this can lead to pulmonary hypertension and chronic breathlessness.
2. Fatigue:
Chronic fatigue is common among those with ASD. The heart’s inefficiency in pumping blood due to the defect means that muscles and organs may not receive adequate oxygen and nutrients, leading to persistent tiredness. This can significantly impact daily activities and overall quality of life.
3. Heart Palpitations:
Many people with ASD report feeling an irregular or unusually fast heartbeat. These palpitations can be due to the extra blood flow through the atrial septum, which can disrupt normal heart rhythms. In some cases, this can lead to arrhythmias that require medical attention.
4. Swelling in the Legs, Feet, or Abdomen:
Fluid retention is a symptom that arises from the heart’s reduced efficiency. As the heart struggles to pump blood effectively, fluid can accumulate in the extremities and abdomen, causing noticeable swelling. This condition, known as edema, can also be a sign of heart failure.
5. Frequent Respiratory Infections:
Children with ASD are particularly prone to recurrent respiratory infections. The defect allows more blood to flow to the lungs, which can cause congestion and create an environment where infections can thrive. This can lead to a cycle of illness and recovery that affects overall health.
6. Heart Murmurs:
A heart murmur is often the first clue to the presence of an ASD. The abnormal flow of blood between the heart’s chambers creates sounds that can be heard through a stethoscope. These murmurs can vary in intensity and may prompt further diagnostic testing to confirm the defect.
7. Poor Growth and Development in Children:
Infants and young children with ASD may exhibit slower growth and developmental delays. The heart defect can affect their overall energy levels and the body’s ability to absorb nutrients efficiently, leading to issues with weight gain and physical milestones.
8. Bluish Skin Color (Cyanosis):
In severe cases, a bluish tint to the skin, lips, or nails can occur. Cyanosis indicates that not enough oxygen-rich blood is being circulated throughout the body. This symptom is more common when there are other heart defects present alongside ASD, compounding the effect on oxygenation.
9. Stroke:
Although less common, ASD can increase the risk of stroke. The defect can allow blood clots to pass from the right to the left side of the heart and then to the brain, leading to a stroke. This risk underscores the importance of monitoring and managing the condition, particularly in adults.
10. Exercise Intolerance:
People with ASD often struggle with physical activities that require endurance. The inefficiency of the heart in delivering oxygenated blood makes sustaining exercise difficult, leading to early fatigue and reduced physical performance. This can discourage participation in sports and other active pursuits.
Reach Dr. Prakash Chandwani, a Heart Doctor in Jaipur for treatment!
For those seeking expert care for Atrial Septal defects (ASD) and other heart conditions, Dr. Prakash Chandwani, a renowned heart doctor in Jaipur, offers comprehensive treatment options. With years of experience and a commitment to patient-centered care, he utilizes the latest diagnostic techniques and treatment modalities to ensure the best outcomes for his patients. Whether it’s a complex heart surgery or a non-invasive procedure, his expertise and compassionate approach provide patients with confidence and comfort. Contact Dr. Prakash Chandwani for top-notch cardiovascular care and take the first step towards a healthier heart.
FAQ: Symptoms of Atrial Septal Defect
1. What causes Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)?
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect, meaning it is present at birth. It occurs when the septum, the wall between the left and right atria, does not form properly during fetal development. The exact cause of ASD is not always known, but it can be associated with genetic factors and environmental influences. Some congenital heart defects, including ASD, may run in families, suggesting a hereditary component.
2. How is ASD diagnosed?
ASD is often diagnosed through a combination of physical examinations and diagnostic tests. A doctor may first detect a heart murmur during a routine check-up, which can prompt further investigation. Diagnostic tests for ASD include echocardiography (an ultrasound of the heart), electrocardiograms (ECG), chest X-rays, and sometimes cardiac MRI or CT scans. These tests help visualize the heart’s structure and confirm the presence of the defect.
3. What treatment options are available for ASD?
The treatment for ASD depends on the size and severity of the defect, as well as the presence of symptoms. Small ASDs may close on their own and require only regular monitoring. Larger defects, however, may need medical intervention. Treatment options include cardiac catheterization, where a device is inserted to close the hole, or open-heart surgery to repair the defect. Medications may also be prescribed to manage symptoms or prevent complications.
4. Can adults develop symptoms of ASD later in life?
Yes, adults can develop symptoms of ASD later in life, even if the defect was not detected during childhood. Small ASDs might go unnoticed for years and only cause issues when the heart’s workload increases with age. Symptoms such as shortness of breath, fatigue, and heart palpitations can manifest as the heart and lungs become less able to compensate for the defect. It is important for adults with unexplained cardiac symptoms to be evaluated for possible congenital heart defects like ASD.
5. What are the potential complications if ASD is left untreated?
If left untreated, ASD can lead to several serious complications. These include pulmonary hypertension (increased blood pressure in the lungs), heart failure, atrial arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), and an increased risk of stroke. Over time, the extra blood flow to the lungs can cause damage to the pulmonary arteries and affect the heart’s ability to function effectively. Early diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial to prevent these complications and ensure a better quality of life.
Also Read; How Stress Affect YOUR HEART?

